Choose any three.
|
SQL As Understood By SQLite
INDEXED BY
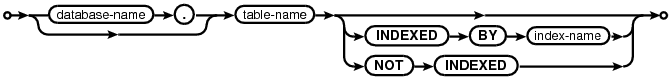
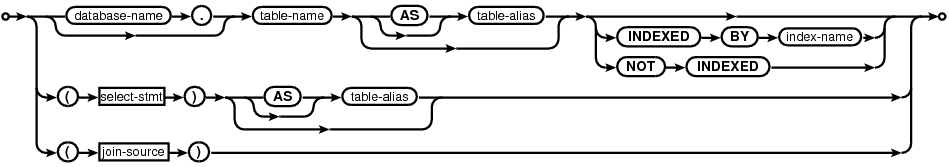
The INDEXED BY phrase is an SQL extension found only in SQLite which can be used to verify that the correct indices are being used on a DELETE, SELECT, or UPDATE statement. The INDEXED BY phrase always follows the name of a table that SQLite will be reading. The INDEXED BY phrase can be seen in the following syntax diagrams:
qualified-table-name:
single-source:
The "INDEXED BY index-name" clause specifies that the named index must be used in order to look up values on the preceding table. If index-name does not exist or cannot be used for the query, then the preparation of the SQL statement fails. The "NOT INDEXED" clause specifies that no index shall be used when accessing the preceding table, including implied indices create by UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY constraints. However, the INTEGER PRIMARY KEY can still be used to look up entries even when "NOT INDEXED" is specified.
Some SQL database engines provide non-standard "hint" mechanisms which can be used to give the query optimizer clues about what indices it should use for a particular statement. The INDEX BY clause of SQLite is not a hinting mechanism and it should not be used as such. The INDEXED BY clause does not give the optimizer hints about which index to use; it gives the optimizer a requirement of which index to use. If the query optimizer is unable to use the index specified by the INDEX BY clause, then the query will fail with an error.
The INDEXED BY clause is not intended for use in tuning the performance of a query. The intent of the INDEXED BY clause is to raise a run-time error if a schema change, such as dropping or creating an index, causes the query plan for a time-sensitive query to change. The INDEXED BY clause is designed to help detect undesirable query plan changes during regression testing. Developers are admonished to omit all use of INDEXED BY during application design, implementation, testing, and tuning. If INDEXED BY is to be used at all, it should be inserted at the very end of the development process when "locking down" a design.
See Also:
The sqlite3_stmt_status() C/C++ interface together with the SQLITE_STMTSTATUS_FULLSCAN_STEP and SQLITE_STMTSTATUS_SORT verbs can be used to detect at run-time when an SQL statement is not making effective use of indices. Many applications may prefer to use the sqlite3_stmt_status() interface to detect index misuse rather than the INDEXED BY phrase described here.