|
ACE
6.1.0
|
|
ACE
6.1.0
|
Implements "barrier synchronization". More...
#include <Barrier.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_Barrier (unsigned int count, const ACE_TCHAR *name=0, void *arg=0) | |
| Initialize the barrier to synchronize count threads. | |
| ~ACE_Barrier (void) | |
| Default destructor. | |
| int | wait (void) |
| int | shutdown (void) |
| void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
Public Attributes | |
| ACE_ALLOC_HOOK_DECLARE | |
| Declare the dynamic allocation hooks. | |
Protected Attributes | |
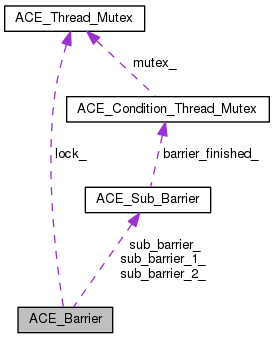
| ACE_Thread_Mutex | lock_ |
| Serialize access to the barrier state. | |
| int | current_generation_ |
| int | count_ |
| Total number of threads that can be waiting at any one time. | |
| ACE_Sub_Barrier | sub_barrier_1_ |
| ACE_Sub_Barrier | sub_barrier_2_ |
| ACE_Sub_Barrier * | sub_barrier_ [2] |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | operator= (const ACE_Barrier &) |
| ACE_Barrier (const ACE_Barrier &) | |
Implements "barrier synchronization".
This class allows <count> number of threads to synchronize their completion of (one round of) a task, which is known as "barrier synchronization". After all the threads call <wait()> on the barrier they are all atomically released and can begin a new round.
This implementation uses a "sub-barrier generation numbering" scheme to avoid overhead and to ensure that all threads wait to leave the barrier correct. This code is based on an article from SunOpsis Vol. 4, No. 1 by Richard Marejka (Richard.Marejka@canada.sun.com).
| ACE_Barrier::ACE_Barrier | ( | unsigned int | count, |
| const ACE_TCHAR * | name = 0, |
||
| void * | arg = 0 |
||
| ) |
Initialize the barrier to synchronize count threads.
| ACE_Barrier::~ACE_Barrier | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Default destructor.
| ACE_Barrier::ACE_Barrier | ( | const ACE_Barrier & | ) | [private] |
| void ACE_Barrier::dump | ( | void | ) | const |
Dump the state of an object.
Reimplemented in ACE_Thread_Barrier.
| void ACE_Barrier::operator= | ( | const ACE_Barrier & | ) | [private] |
| int ACE_Barrier::shutdown | ( | void | ) |
Shut the barrier down, aborting the wait of all waiting threads. Any threads waiting on the barrier when it is shut down will return with value -1, errno ESHUTDOWN.
| 0 | for success, -1 if already shut down. |
| int ACE_Barrier::wait | ( | void | ) |
Block the caller until all count threads have called wait and then allow all the caller threads to continue in parallel.
| 0 | after successfully waiting for all threads to wait. |
| -1 | if an error occurs or the barrier is shut down ( |
Declare the dynamic allocation hooks.
Reimplemented in ACE_Thread_Barrier.
int ACE_Barrier::count_ [protected] |
Total number of threads that can be waiting at any one time.
int ACE_Barrier::current_generation_ [protected] |
Either 0 or 1, depending on whether we are the first generation of waiters or the next generation of waiters.
ACE_Thread_Mutex ACE_Barrier::lock_ [protected] |
Serialize access to the barrier state.
ACE_Sub_Barrier* ACE_Barrier::sub_barrier_[2] [protected] |
ACE_Sub_Barrier ACE_Barrier::sub_barrier_1_ [protected] |
We keep two sub_barriers, one for the first "generation" of waiters, and one for the next "generation" of waiters. This efficiently solves the problem of what to do if all the first generation waiters don't leave the barrier before one of the threads calls wait() again (i.e., starts up the next generation barrier).
ACE_Sub_Barrier ACE_Barrier::sub_barrier_2_ [protected] |
 1.7.5.1
1.7.5.1