|
ACE
6.1.0
|
|
ACE
6.1.0
|
Defines the format and interface for connecting to a peer on a ACE_MEM_Stream object.
More...
#include <MEM_Connector.h>
Public Types | |
| typedef ACE_INET_Addr | PEER_ADDR |
| typedef ACE_MEM_Stream | PEER_STREAM |
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_MEM_Connector (void) | |
| Default constructor. | |
| ACE_MEM_Connector (ACE_MEM_Stream &new_stream, const ACE_INET_Addr &remote_sap, ACE_Time_Value *timeout=0, const ACE_Addr &local_sap=ACE_Addr::sap_any, int reuse_addr=0, int flags=0, int perms=0) | |
| int | connect (ACE_MEM_Stream &new_stream, const ACE_INET_Addr &remote_sap, ACE_Time_Value *timeout=0, const ACE_Addr &local_sap=ACE_Addr::sap_any, int reuse_addr=0, int flags=0, int perms=0) |
| ACE_MEM_IO::Signal_Strategy | preferred_strategy (void) const |
| Get the preferred signaling strategy. | |
| void | preferred_strategy (ACE_MEM_IO::Signal_Strategy strategy) |
| Set the preferred signaling strategy. | |
| void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
Public Attributes | |
| ACE_ALLOC_HOOK_DECLARE | |
| Declare the dynamic allocation hooks. | |
Private Attributes | |
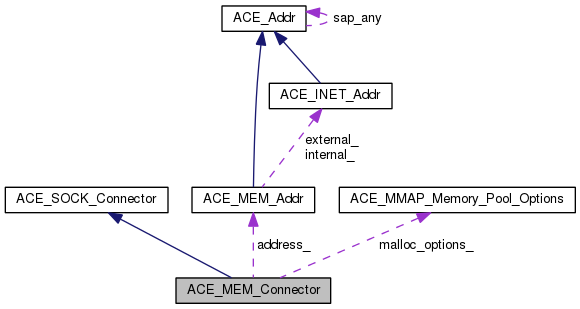
| ACE_MEM_Addr | address_ |
| The acceptor address this connector is connecting to. | |
| ACE_MEM_SAP::MALLOC_OPTIONS | malloc_options_ |
| ACE_MEM_IO::Signal_Strategy | preferred_strategy_ |
| Preferred signaling strategy. | |
Defines the format and interface for connecting to a peer on a ACE_MEM_Stream object.
Reimplemented from ACE_SOCK_Connector.
Reimplemented from ACE_SOCK_Connector.
| ACE_MEM_Connector::ACE_MEM_Connector | ( | void | ) |
Default constructor.
| ACE_MEM_Connector::ACE_MEM_Connector | ( | ACE_MEM_Stream & | new_stream, |
| const ACE_INET_Addr & | remote_sap, | ||
| ACE_Time_Value * | timeout = 0, |
||
| const ACE_Addr & | local_sap = ACE_Addr::sap_any, |
||
| int | reuse_addr = 0, |
||
| int | flags = 0, |
||
| int | perms = 0 |
||
| ) |
Actively connect to a peer, producing a connected ACE_MEM_Stream object if the connection succeeds.
| new_stream | The ACE_MEM_Stream object that will be connected to the peer. |
| remote_sap | The address that we are trying to connect to. The protocol family of remote_sap is used for the connected socket. That is, if remote_sap contains an IPv6 address, a socket with family PF_INET6 will be used, else it will be PF_INET. |
| timeout | Pointer to an ACE_Time_Value object with amount of time to wait to connect. If the pointer is 0 then the call blocks until the connection attempt is complete, whether it succeeds or fails. If *timeout == {0, 0} then the connection is done using nonblocking mode. In this case, if the connection can't be made immediately, this method returns -1 and errno == EWOULDBLOCK. If *timeout > {0, 0} then this is the maximum amount of time to wait before timing out; if the specified amount of time passes before the connection is made, this method returns -1 and errno == ETIME. Note the difference between this case and when a blocking connect is attempted that TCP times out - in the latter case, errno will be ETIMEDOUT. |
| local_sap | (optional) The local address to bind to. If it's the default value of ACE_Addr::sap_any then the OS will choose an unused port. |
| reuse_addr | (optional) If the value is 1, the local address (local_sap) is reused, even if it hasn't been cleaned up yet. |
| flags | Ignored. |
| perms | Ignored. |
| int ACE_MEM_Connector::connect | ( | ACE_MEM_Stream & | new_stream, |
| const ACE_INET_Addr & | remote_sap, | ||
| ACE_Time_Value * | timeout = 0, |
||
| const ACE_Addr & | local_sap = ACE_Addr::sap_any, |
||
| int | reuse_addr = 0, |
||
| int | flags = 0, |
||
| int | perms = 0 |
||
| ) |
Actively connect to a peer, producing a connected ACE_MEM_Stream object if the connection succeeds.
| new_stream | The ACE_MEM_Stream object that will be connected to the peer. |
| remote_sap | The address that we are trying to connect to. The protocol family of remote_sap is used for the connected socket. That is, if remote_sap contains an IPv6 address, a socket with family PF_INET6 will be used, else it will be PF_INET. |
| timeout | Pointer to an ACE_Time_Value object with amount of time to wait to connect. If the pointer is 0 then the call blocks until the connection attempt is complete, whether it succeeds or fails. If *timeout == {0, 0} then the connection is done using nonblocking mode. In this case, if the connection can't be made immediately, this method returns -1 and errno == EWOULDBLOCK. If *timeout > {0, 0} then this is the maximum amount of time to wait before timing out; if the specified amount of time passes before the connection is made, this method returns -1 and errno == ETIME. Note the difference between this case and when a blocking connect is attempted that TCP times out - in the latter case, errno will be ETIMEDOUT. |
| local_sap | (optional) The local address to bind to. If it's the default value of ACE_Addr::sap_any then the OS will choose an unused port. |
| reuse_addr | (optional) If the value is 1, the local address (local_sap) is reused, even if it hasn't been cleaned up yet. |
| flags | Ignored. |
| perms | Ignored. |
| void ACE_MEM_Connector::dump | ( | void | ) | const |
Dump the state of an object.
Reimplemented from ACE_SOCK_Connector.
| ACE_MEM_IO::Signal_Strategy ACE_MEM_Connector::preferred_strategy | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the preferred signaling strategy.
| void ACE_MEM_Connector::preferred_strategy | ( | ACE_MEM_IO::Signal_Strategy | strategy | ) | [inline] |
Set the preferred signaling strategy.
Declare the dynamic allocation hooks.
Reimplemented from ACE_SOCK_Connector.
ACE_MEM_Addr ACE_MEM_Connector::address_ [private] |
The acceptor address this connector is connecting to.
A cached MALLOC_OPTIONS that the MEM_Connector used to initialize the shared memory malloc update connection establishment.
Preferred signaling strategy.
 1.7.5.1
1.7.5.1