|
ACE
6.1.0
|
|
ACE
6.1.0
|
Make a memory pool that is based on mmap(2). This implementation allows memory to be shared between processes.
More...
#include <MMAP_Memory_Pool.h>
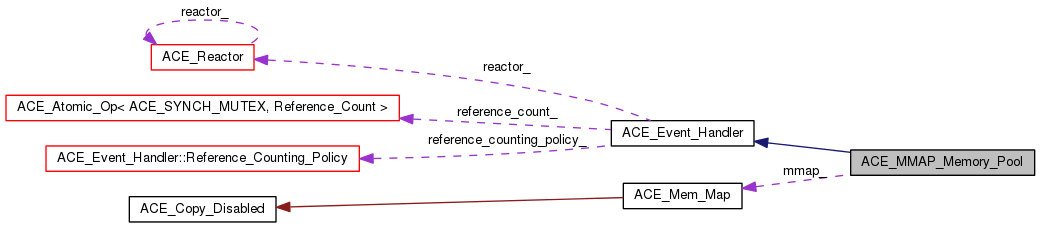
Public Types | |
| typedef ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool_Options | OPTIONS |
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool (const ACE_TCHAR *backing_store_name=0, const OPTIONS *options=0) | |
| Initialize the pool. | |
| virtual | ~ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool (void) |
| Destructor. | |
| virtual void * | init_acquire (size_t nbytes, size_t &rounded_bytes, int &first_time) |
| Ask system for initial chunk of shared memory. | |
| virtual void * | acquire (size_t nbytes, size_t &rounded_bytes) |
| virtual int | release (int destroy=1) |
| Instruct the memory pool to release all of its resources. | |
| virtual int | sync (size_t len, int flags=MS_SYNC) |
| virtual int | sync (int flags=MS_SYNC) |
| virtual int | sync (void *addr, size_t len, int flags=MS_SYNC) |
| Sync the memory region to the backing store starting at addr. | |
| virtual int | protect (size_t len, int prot=PROT_RDWR) |
| virtual int | protect (int prot=PROT_RDWR) |
| virtual int | protect (void *addr, size_t len, int prot=PROT_RDWR) |
| virtual int | seh_selector (void *) |
| virtual int | remap (void *addr) |
| virtual void * | base_addr (void) const |
| Return the base address of this memory pool. | |
| virtual void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
| ACE_Mem_Map const & | mmap (void) const |
| Get reference to underlying ACE_Mem_Map object. | |
| ACE_Mem_Map & | mmap (void) |
| Get reference to underlying ACE_Mem_Map object. | |
Public Attributes | |
| ACE_ALLOC_HOOK_DECLARE | |
| Declare the dynamic allocation hooks. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual size_t | round_up (size_t nbytes) |
| virtual int | commit_backing_store_name (size_t rounded_bytes, size_t &map_size) |
| virtual int | map_file (size_t map_size) |
| Memory map the file up to map_size bytes. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| ACE_Mem_Map | mmap_ |
| Memory-mapping object. | |
| void * | base_addr_ |
| int | use_fixed_addr_ |
Must we use the base_addr_ or can we let mmap(2) select it? | |
| int | flags_ |
| Flags passed into ACE_OS::mmap(). | |
| bool | write_each_page_ |
| size_t | minimum_bytes_ |
| What the minimum bytes of the initial segment should be. | |
| ACE_TCHAR | backing_store_name_ [MAXPATHLEN+1] |
| Name of the backing store where the shared memory pool is kept. | |
| bool | guess_on_fault_ |
| LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES | sa_ |
| Security attributes object, only used on NT. | |
| mode_t | file_mode_ |
| Protection mode for mmaped file. | |
| bool | install_signal_handler_ |
| Should we install a signal handler. | |
Make a memory pool that is based on mmap(2). This implementation allows memory to be shared between processes.
| ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool | ( | const ACE_TCHAR * | backing_store_name = 0, |
| const OPTIONS * | options = 0 |
||
| ) |
Initialize the pool.
| ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::~ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Destructor.
| void * ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::acquire | ( | size_t | nbytes, |
| size_t & | rounded_bytes | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Acquire at least nbytes from the memory pool. rounded_bytes is the actual number of bytes allocated. Also acquires an internal semaphore that ensures proper serialization of ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool initialization across processes.
| void * ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::base_addr | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
Return the base address of this memory pool.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::commit_backing_store_name | ( | size_t | rounded_bytes, |
| size_t & | map_size | ||
| ) | [protected, virtual] |
Compute the new map_size of the backing store and commit the memory.
| void ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::dump | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
Dump the state of an object.
| void * ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::init_acquire | ( | size_t | nbytes, |
| size_t & | rounded_bytes, | ||
| int & | first_time | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Ask system for initial chunk of shared memory.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::map_file | ( | size_t | map_size | ) | [protected, virtual] |
Memory map the file up to map_size bytes.
| ACE_Mem_Map const & ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::mmap | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get reference to underlying ACE_Mem_Map object.
| ACE_Mem_Map & ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::mmap | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Get reference to underlying ACE_Mem_Map object.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::protect | ( | size_t | len, |
| int | prot = PROT_RDWR |
||
| ) | [virtual] |
Change the protection of the pages of the mapped region to prot starting at this->base_addr_ up to len bytes. If len == -1 then change protection of all pages in the mapped region.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::protect | ( | int | prot = PROT_RDWR | ) | [virtual] |
Change the protection of all the pages of the mapped region to prot starting at this->base_addr_.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::protect | ( | void * | addr, |
| size_t | len, | ||
| int | prot = PROT_RDWR |
||
| ) | [virtual] |
Change the protection of the pages of the mapped region to prot starting at addr up to len bytes.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::release | ( | int | destroy = 1 | ) | [virtual] |
Instruct the memory pool to release all of its resources.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::remap | ( | void * | addr | ) | [virtual] |
Try to extend the virtual address space so that addr is now covered by the address mapping. The method succeeds and returns 0 if the backing store has adequate memory to cover this address. Otherwise, it returns -1. This method is typically called by a UNIX signal handler for SIGSEGV or a Win32 structured exception when another process has grown the backing store (and its mapping) and our process now incurs a fault because our mapping isn't in range (yet).
| size_t ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::round_up | ( | size_t | nbytes | ) | [protected, virtual] |
Implement the algorithm for rounding up the request to an appropriate chunksize.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::seh_selector | ( | void * | ep | ) | [virtual] |
Win32 Structural exception selector. The return value decides how to handle memory pool related structural exceptions. Returns 1, 0, or , -1.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::sync | ( | size_t | len, |
| int | flags = MS_SYNC |
||
| ) | [virtual] |
Sync the memory region to the backing store starting at this->base_addr_.
Reimplemented in ACE_Lite_MMAP_Memory_Pool.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::sync | ( | int | flags = MS_SYNC | ) | [virtual] |
Sync the memory region to the backing store starting at this->base_addr_. Will sync as much as the backing file allows.
Reimplemented in ACE_Lite_MMAP_Memory_Pool.
| int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::sync | ( | void * | addr, |
| size_t | len, | ||
| int | flags = MS_SYNC |
||
| ) | [virtual] |
Sync the memory region to the backing store starting at addr.
Sync len bytes of the memory region to the backing store starting at <addr_>.
Reimplemented in ACE_Lite_MMAP_Memory_Pool.
Declare the dynamic allocation hooks.
ACE_TCHAR ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::backing_store_name_[MAXPATHLEN+1] [protected] |
Name of the backing store where the shared memory pool is kept.
void* ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::base_addr_ [protected] |
Base of mapped region. If this has the value of 0 then the OS is free to select any address to map the file, otherwise this value is what the OS must try to use to mmap the file.
mode_t ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::file_mode_ [protected] |
Protection mode for mmaped file.
int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::flags_ [protected] |
Flags passed into ACE_OS::mmap().
bool ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::guess_on_fault_ [protected] |
Try to remap without knowing the faulting address. This parameter is ignored on platforms that know the faulting address (UNIX with SI_ADDR and Win32).
bool ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::install_signal_handler_ [protected] |
Should we install a signal handler.
size_t ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::minimum_bytes_ [protected] |
What the minimum bytes of the initial segment should be.
ACE_Mem_Map ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::mmap_ [protected] |
Memory-mapping object.
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::sa_ [protected] |
Security attributes object, only used on NT.
int ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::use_fixed_addr_ [protected] |
Must we use the base_addr_ or can we let mmap(2) select it?
bool ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::write_each_page_ [protected] |
Should we write a byte to each page to forceably allocate memory for this backing store?
 1.7.5.1
1.7.5.1