|
TAO
2.0.8
|
|
TAO
2.0.8
|
Manager for TAO library services and singleton cleanup. More...
#include <TAO_Singleton_Manager.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual int | init (void) |
| Explicitly initialize. | |
| int | init (int register_with_object_manager) |
| virtual int | fini (void) |
| Explicitly destroy. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static int | starting_up (void) |
| static int | shutting_down (void) |
| static sigset_t * | default_mask (void) |
| static ACE_Thread_Hook * | thread_hook (void) |
| Returns the current thread hook for the process. | |
| static ACE_Thread_Hook * | thread_hook (ACE_Thread_Hook *new_thread_hook) |
| Returns the existing thread hook and assign a new_thread_hook. | |
| static TAO_Singleton_Manager * | instance (void) |
| Accessor to singleton instance. | |
| static int | at_exit (ACE_Cleanup *object, void *param=0, const char *name=0) |
| static int | at_exit (void *object, ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC cleanup_hook, void *param, const char *name) |
Protected Member Functions | |
| TAO_Singleton_Manager (void) | |
| Force allocation on the heap. | |
| ~TAO_Singleton_Manager (void) | |
| Force allocation on the heap. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| int | at_exit_i (void *object, ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC cleanup_hook, void *param, const char *name) |
| TAO_Singleton_Manager (const TAO_Singleton_Manager &) | |
| Disallow copying by not implementing the following ... | |
| TAO_Singleton_Manager & | operator= (const TAO_Singleton_Manager &) |
| Disallow copying by not implementing the following ... | |
Private Attributes | |
| sigset_t * | default_mask_ |
| Default signal set used, for example, in ACE_Sig_Guard. | |
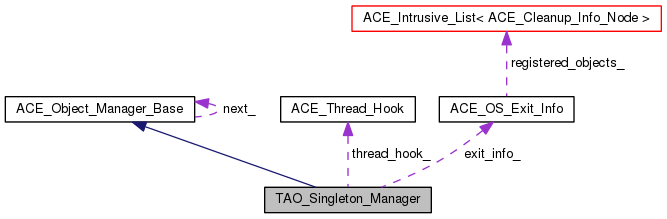
| ACE_Thread_Hook * | thread_hook_ |
| Thread hook that's used by this process. | |
| ACE_OS_Exit_Info | exit_info_ |
| For at_exit support. | |
| int | registered_with_object_manager_ |
Manager for TAO library services and singleton cleanup.
The TAO_Singleton_Manager is basically simplified version of the ACE_Object_Manager. It is designed specifically to manage singletons created by TAO. For example, singleton instances created by TAO will be automatically registered with the singleton instance of this Singleton Manager.
| TAO_Singleton_Manager::TAO_Singleton_Manager | ( | void | ) | [protected] |
Force allocation on the heap.
| TAO_Singleton_Manager::~TAO_Singleton_Manager | ( | void | ) | [protected] |
Force allocation on the heap.
| TAO_Singleton_Manager::TAO_Singleton_Manager | ( | const TAO_Singleton_Manager & | ) | [private] |
Disallow copying by not implementing the following ...
| int TAO_Singleton_Manager::at_exit | ( | ACE_Cleanup * | object, |
| void * | param = 0, |
||
| const char * | name = 0 |
||
| ) | [static] |
Register an ACE_Cleanup object for cleanup at process termination. The object is deleted via the ace_cleanup_destroyer. If you need more flexiblity, see the other at_exit method below. For OS's that do not have processes, cleanup takes place at the end of main. Returns 0 on success. On failure, returns -1 and sets errno to: EAGAIN if shutting down, ENOMEM if insufficient virtual memory, or EEXIST if the object (or array) had already been registered.
| int TAO_Singleton_Manager::at_exit | ( | void * | object, |
| ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC | cleanup_hook, | ||
| void * | param, | ||
| const char * | name | ||
| ) | [static] |
Register an object (or array) for cleanup at process termination. cleanup_hook points to a (global, or static member) function that is called for the object or array when it to be destroyed. It may perform any necessary cleanup specific for that object or its class. param is passed as the second parameter to the cleanup_hook function; the first parameter is the object (or array) to be destroyed. cleanup_hook, for example, may delete the object (or array). For OS's that do not have processes, this function is the same as at_thread_exit. Returns 0 on success. On failure, returns -1 and sets errno to: EAGAIN if shutting down, ENOMEM if insufficient virtual memory, or EEXIST if the object (or array) had already been registered.
| int TAO_Singleton_Manager::at_exit_i | ( | void * | object, |
| ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC | cleanup_hook, | ||
| void * | param, | ||
| const char * | name | ||
| ) | [private] |
Register an object or array for deletion at program termination. See description of static version above for return values.
| sigset_t * TAO_Singleton_Manager::default_mask | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Accesses a default signal set used, for example, in ACE_Sig_Guard methods.
| int TAO_Singleton_Manager::fini | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Explicitly destroy.
Implements ACE_Object_Manager_Base.
| int TAO_Singleton_Manager::init | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Explicitly initialize.
Implements ACE_Object_Manager_Base.
| int TAO_Singleton_Manager::init | ( | int | register_with_object_manager | ) |
Explicitly initialize the TAO_Singleton_Manager, in addition to explicitly registering (or not registering) with the ACE_Object_Manager.
| TAO_Singleton_Manager * TAO_Singleton_Manager::instance | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Accessor to singleton instance.
| TAO_Singleton_Manager& TAO_Singleton_Manager::operator= | ( | const TAO_Singleton_Manager & | ) | [private] |
Disallow copying by not implementing the following ...
| int TAO_Singleton_Manager::shutting_down | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Returns 1 after the TAO_Singleton_Manager has been destroyed. See ACE_Object_Manager::shutting_down for more information.
| int TAO_Singleton_Manager::starting_up | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Returns 1 before the TAO_Singleton_Manager has been constructed. See ACE_Object_Manager::starting_up for more information.
| ACE_Thread_Hook * TAO_Singleton_Manager::thread_hook | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Returns the current thread hook for the process.
| ACE_Thread_Hook * TAO_Singleton_Manager::thread_hook | ( | ACE_Thread_Hook * | new_thread_hook | ) | [static] |
Returns the existing thread hook and assign a new_thread_hook.
sigset_t* TAO_Singleton_Manager::default_mask_ [private] |
Default signal set used, for example, in ACE_Sig_Guard.
For at_exit support.
int TAO_Singleton_Manager::registered_with_object_manager_ [private] |
Indicates if TAO_Singleton_Manager is registered with the ACE_Object_Manager.
Thread hook that's used by this process.
 1.7.5.1
1.7.5.1