| CONTENTS | PREV | NEXT | Java Object Serialization Specification version 6.0 |
CHAPTER 4 |
ObjectStreamClass
provides information about classes that are saved in a
Serialization stream. The descriptor provides the fully-qualified
name of the class and its serialization version UID. A
SerialVersionUID identifies the unique original class
version for which this class is capable of writing streams and from
which it can read.
package java.io;
public class ObjectStreamClass
{
public static ObjectStreamClass lookup(Class cl);
public static ObjectStreamClass lookupAny(Class cl);
public String getName();
public Class forClass();
public ObjectStreamField[] getFields();
public long getSerialVersionUID();
public String toString();
}
The lookup method returns
the ObjectStreamClass descriptor for the specified
class in the virtual machine. If the class has defined
serialVersionUID it is retrieved from the class. If
the serialVersionUID is not defined by the class, it
is computed from the definition of the class in the virtual
machine. If the specified class is not serializable or
externalizable, null is returned.
The lookupAny method
behaves like the lookup method, except that it returns
the descriptor for any class, regardless of whether it implements
Serializable. The serialVersionUID of a
class that does not implement Serializable is
0L.
The getName method
returns the name of the class, in the same format that is used by
the Class.getName method.
The forClass method
returns the Class in the local virtual machine if one
was found by ObjectInputStream.resolveClass method.
Otherwise, it returns null.
The getFields method
returns an array of ObjectStreamField objects that
represent the serializable fields of this class.
The getSerialVersionUID
method returns the serialVersionUID of this class.
Refer to Section 4.6, "Stream
Unique Identifiers." If not specified by the class, the
value returned is a hash computed from the class's name,
interfaces, methods, and fields using the Secure Hash Algorithm
(SHA) as defined by the National Institute of Standards.
The toString method returns a printable
representation of the class descriptor including the name of the
class and the serialVersionUID.
ObjectStreamClass descriptors are also used to provide information about dynamic proxy classes (e.g., classes obtained via calls to the getProxyClass method of java.lang.reflect.Proxy) saved in a serialization stream. A dynamic proxy class itself has no serializable fields and a serialVersionUID of 0L. In other words, when the Class object for a dynamic proxy class is passed to the static lookup method of ObjectStreamClass, the returned ObjectStreamClass instance will have the following properties:
When an ObjectStreamClass instance that does not
represent a dynamic proxy class is written to the stream, it writes
the class name and serialVersionUID, flags, and the
number of fields. Depending on the class, additional information
may be written:
SC_SERIALIZABLE nor the SC_EXTERNALIZABLE
flag bits are set.SC_SERIALIZABLE flag is set, the number of fields
counts the number of serializable fields and is followed by a
descriptor for each serializable field. The descriptors are written
in canonical order. The descriptors for primitive typed fields are
written first sorted by field name followed by descriptors for the
object typed fields sorted by field name. The names are sorted
using String.compareTo. For details of the format,
refer to Section 6.4,
"Grammar for the Stream Format".SC_EXTERNALIZABLE flag, and the number of
fields is always zero.SC_ENUM flag, and the number of fields is always
zero.The serialized representations of ObjectStreamClass descriptors for dynamic proxy classes and non-dynamic proxy classes are differentiated through the use of different typecodes (TC_PROXYCLASSDESC and TC_CLASSDESC, respectively); for a more detailed specification of the grammar, see Section 6.4, "Grammar for the Stream Format".
ObjectStreamField
represents a serializable field of a serializable class. The
serializable fields of a class can be retrieved from the
ObjectStreamClass.
The special static serializable
field, serialPersistentFields, is an array of
ObjectStreamField components that is used to override
the default serializable fields.
package java.io;
public class ObjectStreamField implements Comparable {
public ObjectStreamField(String fieldName,
Class fieldType);
public ObjectStreamField(String fieldName,
Class fieldType,
boolean unshared);
public String getName();
public Class getType();
public String getTypeString();
public char getTypeCode();
public boolean isPrimitive();
public boolean isUnshared();
public int getOffset();
protected void setOffset(int offset);
public int compareTo(Object obj);
public String toString();
}
ObjectStreamField objects
are used to specify the serializable fields of a class or to
describe the fields present in a stream. Its constructors accept
arguments describing the field to represent: a string specifying
the name of the field, a Class object specifying the
type of the field, and a boolean flag (implicitly
false for the two-argument constructor) indicating
whether or not values of the represented field should be read and
written as "unshared" objects if default
serialization/deserialization is in use (see the descriptions of
the ObjectInputStream.readUnshared and
ObjectOutputStream.writeUnshared methods in sections
3.1 and 2.1, respectively).
The getName method
returns the name of the serializable field.
The getType method
returns the type of the field.
The getTypeString
method returns the type signature of the field.
The getTypeCode method
returns a character encoding of the field type
(`B' for byte, `C'
for char, `D' for
double, `F' for float,
`I' for int, `J' for
long, `L' for non-array object types,
`S' for short, `Z'
for boolean, and `[` for arrays).
The isPrimitive method
returns true if the field is of primitive type, or
false otherwise.
The isUnshared method
returns true if values of the field should be written
as "unshared" objects, or false otherwise.
The getOffset method
returns the offset of the field's value within instance data of
the class defining the field.
The setOffset method
allows ObjectStreamField subclasses to modify the
offset value returned by the getOffset method.
The compareTo method
compares ObjectStreamFields for use in sorting.
Primitive fields are ranked as "smaller" than non-primitive
fields; fields otherwise equal are ranked alphabetically.
The toString method returns a printable
representation with name and type.
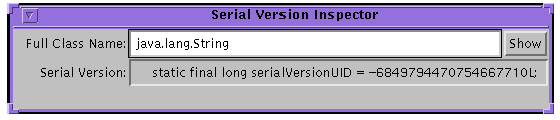
serialVersionUID. When invoked with the-show option,
it puts up a simple user interface. To find out if a class is
serializable and to find out its
serialVersionUID, enter its full class name,
then press either the Enter or the Show button. The string printed
can be copied and pasted into the evolved class.
When invoked on the command line with one or more class names,
serialver prints the serialVersionUID for each class
in a form suitable for copying into an evolving class. When invoked
with no arguments, it prints a usage line.
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3487495895819393L;
The stream-unique identifier is a 64-bit hash of the class name,
interface class names, methods, and fields. The value must be
declared in all versions of a class except the first. It may be
declared in the original class but is not required. The value is
fixed for all compatible classes. If the SUID is not declared for a
class, the value defaults to the hash for that class. The
serialVersionUID for dynamic proxy classes and enum
types always have the value 0L. Array classes cannot
declare an explicit serialVersionUID, so they always
have the default computed value, but the requirement for matching
serialVersionUID values is waived for array
classes.
serialVersionUID values, since the default
serialVersionUID computation is highly sensitive to
class details that may vary depending on compiler implementations,
and can thus result in unexpected serialVersionUID
conflicts during deserialization, causing deserialization to fail.
Externalizable class must output a stream data format
that is extensible in the future. The initial version of the method
readExternal has to be able to read the output format
of all future versions of the method writeExternal.
The serialVersionUID is
computed using the signature of a stream of bytes that reflect the
class definition. The National Institute of Standards and
Technology (NIST) Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA-1) is used to compute
a signature for the stream. The first two 32-bit quantities are
used to form a 64-bit hash. A
java.lang.DataOutputStream is used to convert
primitive data types to a sequence of bytes. The values input to
the stream are defined by the Java Virtual Machine (VM)
specification for classes. Class modifiers may include the
ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_FINAL,
ACC_INTERFACE, and ACC_ABSTRACT flags;
other flags are ignored and do not affect
serialVersionUID computation. Similarly, for field
modifiers, only the ACC_PUBLIC,
ACC_PRIVATE, ACC_PROTECTED,
ACC_STATIC, ACC_FINAL,
ACC_VOLATILE, and ACC_TRANSIENT flags are
used when computing serialVersionUID values. For
constructor and method modifiers, only the ACC_PUBLIC,
ACC_PRIVATE, ACC_PROTECTED,
ACC_STATIC, ACC_FINAL,
ACC_SYNCHRONIZED, ACC_NATIVE,
ACC_ABSTRACT and ACC_STRICT flags are
used. Names and descriptors are written in the format used by the
java.io.DataOutputStream.writeUTF method.
The sequence of items in the stream is as follows:
private static and private transient
fields:
<clinit>.java.lang.reflect.Modifier.STATIC, written as a 32-bit
integer.()V.private constructor sorted by method
name and signature:
<init>.private method sorted by method name
and signature:
DataOutputStream and produces five 32-bit values
sha[0..4].H0 H1 H2 H3 H4, is in an
array of five int values named sha, the
hash value would be computed as follows:
long hash = ((sha[0] >>> 24) & 0xFF) |
((sha[0] >>> 16) & 0xFF) << 8 |
((sha[0] >>> 8) & 0xFF) << 16 |
((sha[0] >>> 0) & 0xFF) << 24 |
((sha[1] >>> 24) & 0xFF) << 32 |
((sha[1] >>> 16) & 0xFF) << 40 |
((sha[1] >>> 8) & 0xFF) << 48 |
((sha[1] >>> 0) & 0xFF) << 56;